E-E-A-T and SEO: A Comprehensive Guide (2025 Update)
E-E-A-T and SEO: How to Build Trust and Authority with Google
E-E-A-T, which stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, is a crucial concept in Search Engine Optimization. In fact, since 2022, Google has confirmed that E-A-T (now with the added ‘E’ for Experience) is evaluated for every search query. This concept is thoroughly detailed within the Google Search Quality Rater Guidelines, a document that provides insights into how Google assesses content quality. Understanding E-E-A-T is essential for effective content marketing and building website authority, as Google itself advises that understanding these guidelines can help you improve your own content.
E-E-A-T is a measure of the legitimacy of your entity as a destination for the topics you cover.
Think of how important it is in today’s world to be recognized as authentic!
Experience
Experience is crucial because search engines aim to provide users with results from sources that have practical, first-hand knowledge. Content demonstrating experience, like detailed product reviews based on actual use, or travel guides written by someone who has visited the place, is more likely to rank higher for queries seeking real-world perspectives. Often content that comes from businesses with a real-world presence and in-store customers does well.
Expertise
Expertise is vital for SEO, especially in YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics. Google prioritizes content created by subject matter experts because inaccurate or unqualified advice in these areas can be harmful. Demonstrating expertise through credentials, professional background, or in-depth, technically accurate content signals to Google that your page is a reliable source of information, improving its ranking potential for expertise-seeking queries.
Authoritativeness
Authoritativeness in the SEO context means being recognized as a go-to source of information within your industry or niche. When other reputable websites and experts in your field recognize you as an authority (through links, citations, mentions), it boosts your SEO. Google interprets these external signals as validation of your content’s quality and relevance, leading to improved rankings for topic-related searches.
For more, read the rater guidelines and search for “reputation” and also “known for”. Being known as a go-to source for your topics is so important!
Trustworthiness
Trustworthiness is fundamental for SEO success, as Google wants to direct users to sources they can rely on. A trustworthy website is secure, transparent in its practices, and has a positive reputation. Signals of trustworthiness, such as HTTPS, clear contact information, privacy policies, and positive user reviews, contribute to a website’s overall SEO performance by increasing user confidence and Google’s assessment of its reliability.
A few negative reviews is not likely to cause trust issues. But, if there is overwhelming negative sentiment against your brand, this can possibly impact your ability to rank for your queries.
(By the way, if you’re an SEO who is looking for a job, check out Nick’s mock interview questions.)
How my understanding of E-E-A-T has changed over the years
Google’s HJ Kim tells us E-A-T (now E-E-A-T is the template Google uses to rate every site for every query.)
Today I think of E-E-A-T like a template that uses the signals available to Google to create an idea of which content has the qualities of authenticity a searcher would expect for each particular query.
A search for a medical query will be identified as needing a response from an entity known for their medical expertise.
A search for a product review might be identified as best served by content that the signals on the web indicate has the appropriate experience and recognized authority to speak on this topic.
Let’s talk about signals.
Signals
For years, our attempts at improving E-E-A-T revolved around improving the signals on the web that search engines were likely to use in their assessments. We used our knowledge of what we knew as SEO’s to be signals important to Google’s algorithms. The most famous of these signals is links. We also looked at things mentioned in the rater guidelines and in Google’s documentation that could possibly be used as signals by an algorithm. My advice for years has, and still is, to do things that improve how your audience perceives and trusts you and finds you helpful.
But this has been, until recently, difficult to translate into defendable SEO advice, beyond, “Hey, this is what Google told us they aim to reward.”
In 2018, I asked Gary Illyes from Google how E-A-T was determined:

What signals are important to E-E-A-T?
Backlinks
High-quality backlinks from authoritative websites in your industry are a strong positive signal. For example, a medical website getting backlinks from reputable medical journals or university websites signals expertise and authoritativeness in the medical field. In this age of SEO in 2025, Google is quite good at knowing if a backlink is truly a recommendation from a reputable source or one simply made to manipulate rankings.
Mentions/Citations without links
Brand mentions or author mentions on reputable news sites, industry publications, or expert blogs, even without a direct link, can signal authority and recognition within your field. If your brand or authors are frequently cited as sources in respected publications, it suggests you are seen as a trustworthy source of information.
Lack of mentions, or mentions only in low-quality or spammy contexts, may be a negative signal in Google’s eyes.
Reputation/Reviews
Consistently positive reviews and high ratings on reputable review platforms (like Google Business Profile, Yelp, industry-specific review sites) signal trustworthiness and customer satisfaction. A business with overwhelmingly positive reviews is seen as more trustworthy. However, not all businesses are the type that get reviews, so this may not be applicable to you.
Numerous negative reviews, complaints on consumer protection sites, or a pattern of unresolved customer issues are strong negative signals for trustworthiness and can significantly harm perceived E-E-A-T.
Author bios
Clearly presented author bios with credentials, affiliations, and demonstrable expertise relevant to the content topic can be positive on-site signals for expertise. For example, a doctor writing medical content should have their medical credentials and experience clearly visible. Author bios are not directly ranking factors. Author bios help readers understand the expertise of your authors, and I believe they also help Google determine if authoritative entities are connected with your brand.
Do you need author bios? It doesn’t hurt! I always like to extol the qualifications of authors.
User engagement
I expect that user engagement can send signals to Google as well. Do people consistently choose your content? Do they engage with it? Do they find it to be the satisfying answer to their query? These things are important. For more on this, read my post on Navboost that talks about Google’s use of clicks and other user engagement signals.
What do the Quality Raters’ Guidelines (QRG) say about E-A-T?
Google’s quality rater guidelines, also known as the search quality evaluator guidelines, are available for anyone to read. Google updates the wording in this document a couple of times a year.
This document is loaded with discussions on Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness. We want to pay attention to this information as Google has told us that these guidelines are a key to helping us understand what Google wants to see on a website in terms of quality.
In a CNBC interview, Google’s VP of Search, Ben Gomes was asked about the connection between Google’s Quality Raters’ Guidelines and Google’s algorithms. He said:
“You can view the raters’ guidelines as where we want the search algorithm to go. They don’t tell you how the algorithm is ranking results, but they fundamentally show what the algorithm should do.”
If you have ever wondered what it is that Google considers “high quality”, the QRG is actually a textbook that explains this in great detail!
While Google’s algorithms are not an exact representation of what is in the QRG, as mentioned above, the QRG reflect what Google wants the algorithms to do. And there is a LOT of information about Google E-A-T in these guidelines.
Let’s look at what the QRG say about E-A-T. The following screenshots are all taken directly from the latest version of the guidelines, which at the time of publishing this article is the version released on July 28, 2022. E-A-T is mentioned in these guidelines 130 times! (Note from 2024 Marie. Here’s the newest version. Read it!)
Google's E-A-T Guidelines
Google says that E-A-T is very important. The raters are given many guidelines to consider when it comes to evaluating E-A-T. While we don’t know exactly what factors Google’s algorithms measure, we can learn to demonstrate good E-A-T by reading these recommendations.

E-A-T is extremely important for Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) sites
E-E-A-T is not just important for YMYL sites – it is absolutely critical. For websites covering topics that could impact a user’s health, financial stability, safety, or well-being, Google has an exceptionally high bar for quality and trustworthiness. This is because inaccurate, misleading, or low-quality information in YMYL areas can have serious, real-world consequences for users. Imagine someone making critical health decisions based on flawed medical advice found online, or losing their life savings due to poor financial guidance from an untrustworthy source. The potential for harm is significant, and Google’s algorithms are designed to minimize these risks by prioritizing highly E-E-A-T-rich content for YMYL queries.
Important to know for sites writing on YMYL topics:
- Medical websites should feature content written or reviewed by board-certified doctors, clearly displaying their credentials, affiliations, and experience. Legal sites should be authored by licensed attorneys. Financial sites by certified financial advisors, and so on. Detailed author bios are essential, linking to professional profiles or organization directories that verify their expertise.
- YMYL content, especially in health and finance, should be rigorously supported by scientific evidence and data. Medical articles should cite peer-reviewed studies and reputable medical organizations. Financial advice should be grounded in established financial principles and regulations. Clearly cite sources and link to them to enhance transparency and demonstrate a basis in expertise.
- YMYL information needs to be current and reflect the latest consensus in the relevant field. Medical websites should be regularly updated to reflect new research and treatment guidelines. Financial advice should account for current market conditions and regulatory changes. Clearly display ‘last updated’ dates and implement a process for regular content review.
- For YMYL sites, especially those handling personal or financial data, robust website security (HTTPS, security certifications) and a clear, comprehensive privacy policy are non-negotiable. These demonstrate a commitment to protecting user information and building trust.
Here’s more from the QRG:
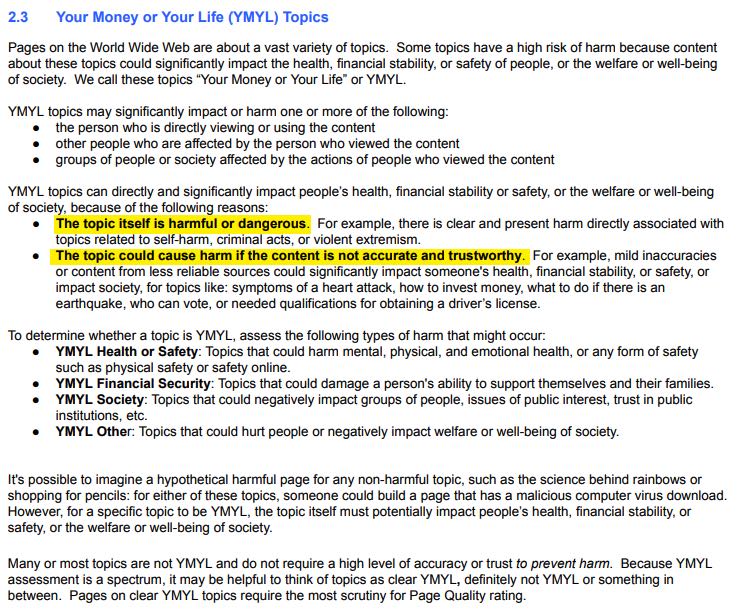
The QRG tell us that YMYL content that is lacking E-A-T is to be considered low quality.

Even if your topic is not an obvious YMYL topic, we still would recommend paying attention to Google E-A-T.
Did you know that Google has a list of characteristics of high quality pages?
The QRG list a high level of E-A-T as the first characteristic of a high quality page.

Author E-A-T can matter (for many, but not all sites)
Displaying your author information on your website can help your readers understand that your content comes from a place of quality and authenticity. Schema, including sameas schema can help search engines understand which entities are associated with your business. These can indirectly help provide more signals and clarity surrounding your qualifications on your topic.
The signals that Google use to determine E-A-T can likely be applied to brands, to websites, to businesses, and also to authors. Most likely, Google’s knowledge graph helps Google evaluate many signals connected to E-A-T. I believe that as an author starts to become mentioned by other experts or authorities online, this can help create relationships in the knowledge graph.
Google is looking for signals to measure that demonstrate your content is created from a position of expertise. In some cases, a website itself may be known for having expertise on a topic. In others, the expertise of the author themselves might be considered.
The QRG tell us that if the creator of the main content (MC), or in other words, the author, is lacking expertise for the topic, the page should be rated as low quality.

This is extremely important! Think of how many sites writing on YMYL topics have articles that are written by people who are fantastic journalists, but who have no actual real life experience on the topic on which they are writing. This might be ok if you have a level of authority that people would expect as acceptable to write on a topic.
For example, a news outlet like Forbes might have an article ranking written by a journalist who lacks first hand expertise. But, there is a level of trust and authority that comes by being known as a news organization with editorial standards.
What you need to ask yourself is this:
For your topics, do others online truly recognize either your website or your authors as a reliable destination for information on the topics you cover?
If not, you are lacking in E-A-T. Ranking will be difficult.
The QRG are loaded with examples of articles that Google considers low quality because of a lack of author E-A-T.
This screenshot is from the QRG:
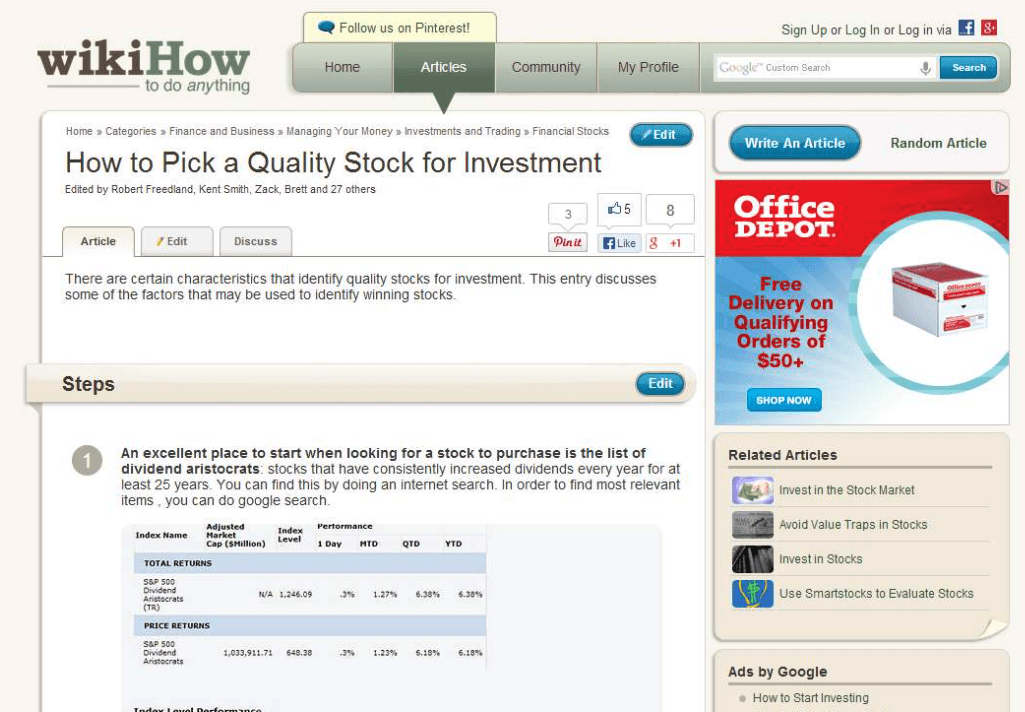
You can see that this is an article about a financial topic. Here is how the raters are instructed to assess a page like this:
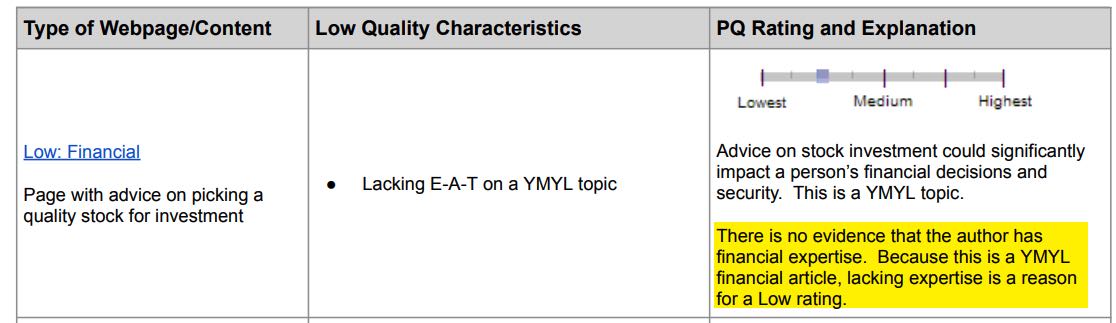
“There is no evidence that the author has financial expertise. Because this is a YMYL financial article, lacking expertise is a reason for a Low rating.”
As such, I think that it is vitally important for many sites that every author on your site has a thorough author bio that talks about why they are qualified to write on this subject. The exception is for sites where the site itself is widely known for their subjects.
The Knot is known for writing on wedding topics.
Search Engine Land is known for SEO topics.
IBM is known for topics related to computers.
Google’s algorithms know that content produced on these sites is often referenced by other experts or by other users. These sites can publish content without author bios and likely it will not suffer. Still, if I were creating content for these sites, I would not rely on my brand authority to demonstrate E-A-T. I want to give Google and my readers as many signals as I can to help them understand that my content is written from the perspective of people who know their stuff on these topics.
If you want to rank for queries where first hand expertise is important, unless your brand is very well known, you likely can benefit from adding author bios to help your readers and also Google understand their expertise. That is, however, assuming that your authors truly do have expertise.
You should link these author bios to an author page that goes into even greater detail. I also recommend implementing author schema and sameAs schema to give Google as much information as possible on your authors and where other expert or authoritative sites have recognized their expertise.
Here is another example from the QRG of an author who is lacking expertise:
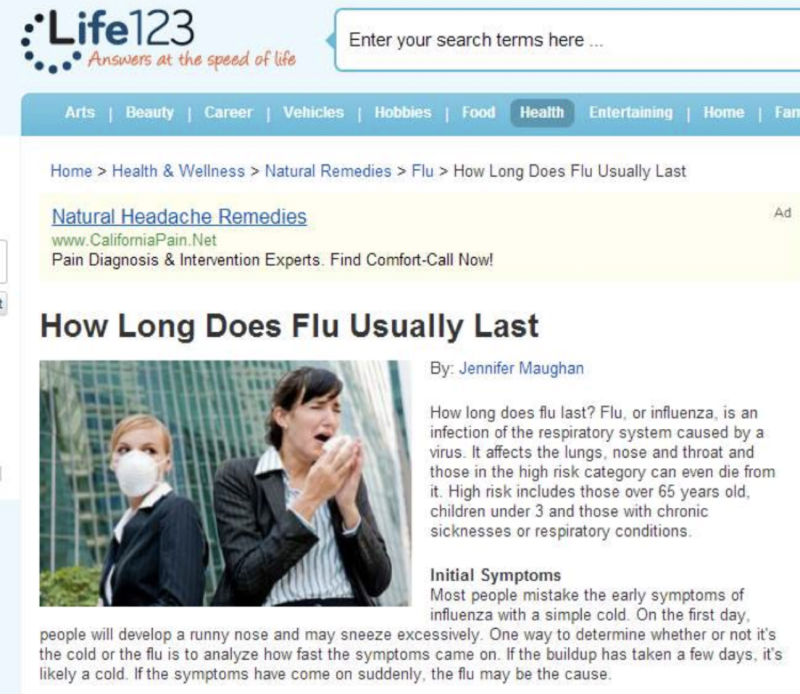
If you Google this author’s name, you will find that she is known as a content writer, but there is very little evidence that she has expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness as a medical writer.
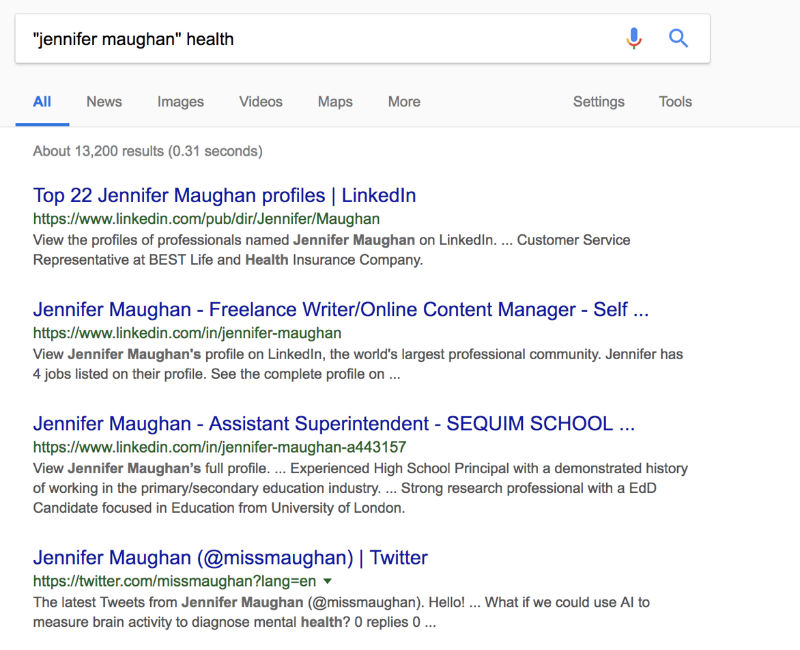
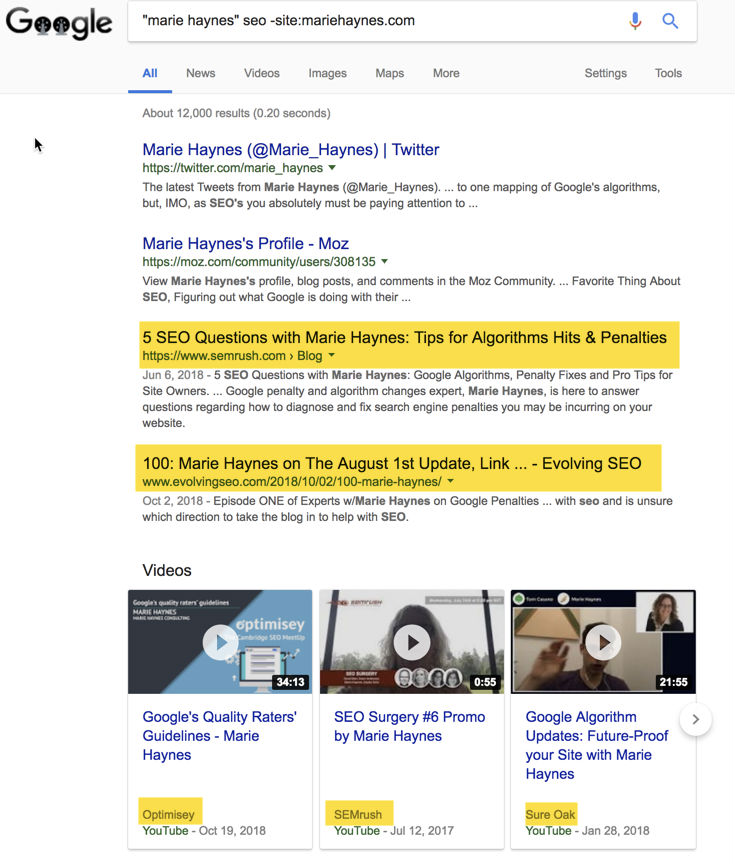
Note: I recommend that you do this kind of search for your authors. Google their name. You may need to add a keyword if they have a common name. You’ll also want to use a negative site query so that you don’t just see posts from their sites. For example, here is a search for “marie haynes” seo -site:mariehaynes.com.
You can see that I am mentioned in places that are recognized as authoritative for SEO:
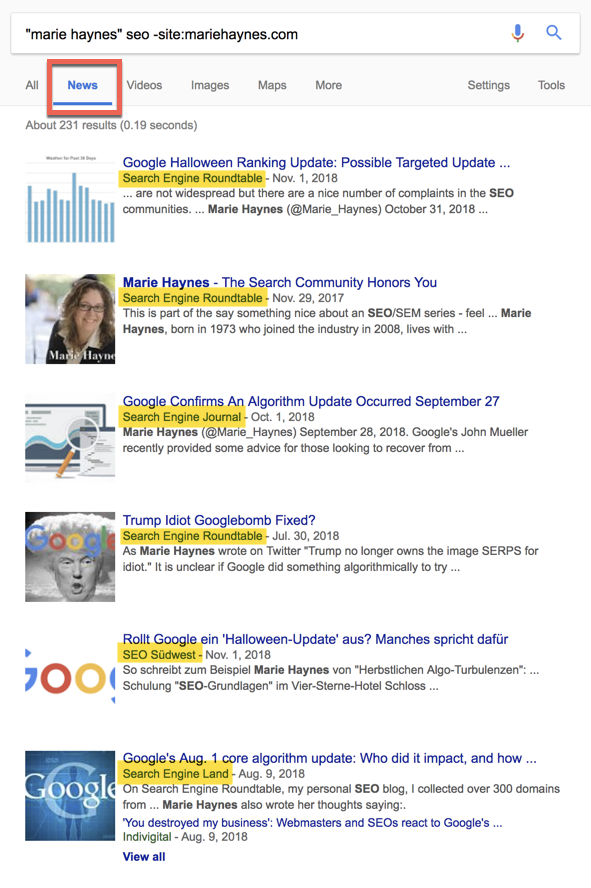
Another great way to check for perceived authority is to do the same search on Google News. You can see here that I have a couple of hundred mentions in Google news for my name in connection with SEO:
I did this same search for one of my colleagues, Dylan. Even though Dylan is really good at SEO and has a lot of knowledge, he is likely seen as lacking in E-A-T for this topic because there is no one else mentioning him online.
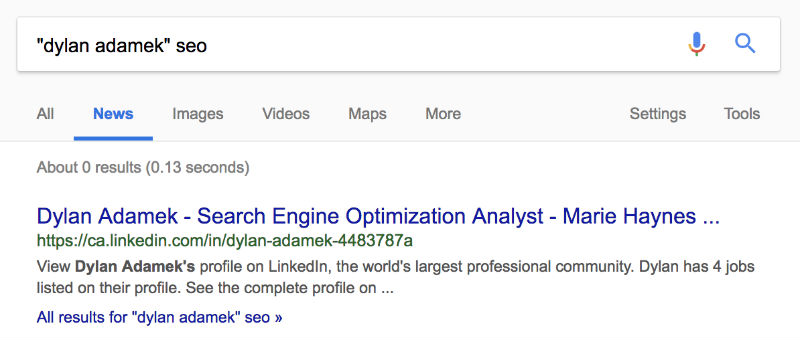
This doesn’t mean that Dylan is not good at SEO. (The opposite is true!) But, if he wanted to start publishing SEO articles, they likely would not rank well until he builds up online authority for his knowledge on this topic.
Going back to the example in the QRG, with the author who has written about the flu, this is what the QRG say about her:

“There is no evidence that the author has medical expertise. Because this is a YMYL medical article, lacking expertise is a reason for a Low rating.”
I believe it is vitally important that your authors are recognized as an authority in your vertical.

Characteristics of a Low Quality Page
The very first characteristic of a low quality page listed in the QRG is a lack of E-A-T.

How does Google measure E-A-T algorithmically?
Google tells us in their documentation on How Search Works that there are several steps to the ranking process:
- They understand the meaning of your query.
- They find content in their index that is relevant to your query. (How they do this is a whole other fascinating discussion. Google’s new documentation on how their systems work tell us that AI called RankBrain helps Google understand concepts in queries. And neural matching helps Google find pages that cover those concepts. And passage ranking helps them find individual sections of pages that are relevant. Update by 2024 Marie: There is so much more to know. I’d encourage you to read the Pandu Nayak testimony in the DOJ vs Google case, or join us in the Search Bar where we are talking about how AI systems like RankBrain, DeepRank and RankEmbed BERT are changing Search. You can read some of the discussion by clicking that link, but much of it is in the paid, private area, Search Bar Pro.
It’s the next step that we are most interested in here. Google calls it “Quality of content”. To determine content quality, they identify signals they can use to determine which content demonstrates E-E-A-T. We learned above that Google calls E-E-A-T the template by which they rate every site for every query.

When Google runs a core update they tell us to focus on two things:
- Focus on content. They gave us a whole list of questions to assess to help us do this.
- Get to know the quality rater guidelines and R-E-A-T
(I am honoured that Google linked to this very page you are reading now in their recommendations on where to go to understand more on E-A-T.)
They recently added even more questions for us to consider to help us determine if we are producing content that is helpful.
Many of the “helpful content questions” relate to E-A-T:
Update by 2024 Marie. I used to treat these questions like a checklist and surmise how Google’s systems could measure each of them. I’ve realized now that this is a list of the types of things that people tend to like and find helpful. Content that reflects these ideals is more likely to do well in Google’s machine learned systems that work to rank and reward reliable and helpful content.
- Does the content present information in a way that makes you want to trust it, such as clear sourcing, evidence of the expertise involved, background about the author or the site that publishes it, such as through links to an author page or a site’s About page?
- If someone researched the site producing the content, would they come away with an impression that it is well-trusted or widely-recognized as an authority on its topic?
- Is this content written by an expert or enthusiast who demonstrably knows the topic well?
- Do you have an existing or intended audience for your business or site that would find the content useful if they came directly to you?
- Does your content clearly demonstrate first-hand expertise and a depth of knowledge (for example, expertise that comes from having actually used a product or service, or visiting a place)?
- Did you decide to enter some niche topic area without any real expertise, but instead mainly because you thought you’d get search traffic?
How to improve Google E-E-A-T
We have established that E-E-A-T is an important part of Google’s algorithms. A lack of E-E-A-T makes it very hard to rank. So, does this mean that only sites recognized as authorities can rank well? Is there nothing else that can be done?
E-E-A-T can definitely be improved upon. At the end of this article I will share examples of sites that we believed saw ranking improvements after implementing our E-E-A-T suggestions.
To discuss ways of improving E-A-T, we’ll look again at quotes that come from the QRG. Here are several things that are suggested in the QRG that can give us clues to how Google might assess E-A-T.
Not all of these are important for every niche though. For an E-Commerce store, reviews could be seen as a sign of the store’s popularity. For a doctor’s website, Google is more likely to look to signals demonstrating real life expertise in medicine. Still, each of these should be considered for your site:
1) Get good reviews
What people say about your business online matters. Here is how the quality raters are instructed to do reputation research:

They are told to look at Yelp, the BBB, Amazon and Google Shopping amongst other sources:

This does not mean that a high rating on the BBB is going to make you rank better. It would likely be just one of the many signals Google considers when a searcher does a query for which a site’s reputation is important.
If you have the odd bad review, that is not likely to hurt you:

But, if it is obvious that most people who are reviewing your business online are complaining, then I believe that this can affect Google’s assessment of quality for your site.
Here are some factors that we look at based on things described in the QRG:
- Do competitors have significantly more reviews online? If more people are talking about your competitors, then this might be a sign that they are more highly recognized as an authority than you are.
- Do competitors have a much larger number of positive reviews than you do?
- Is the general overall sentiment of reviews negative?
2) Get Wikipedia mentions, or better yet, your own page (but that’s hard)
Wikipedia is mentioned a lot in the QRG. It is clear that Google recognizes it as a trusted site. In the past, SEOs would often say that links from Wikipedia don’t matter as they are nofollowed links and don’t pass any PageRank. But, now that we know Google has many systems they use beyond PageRank it is not hard to imagine why Wikipedia mentions could speak to a business’ legitimacy. Wikipedia mentions contribute to the knowledge graph.
Getting your own Wikipedia page is really hard. You have to meet Wikipedia’s standards on notability which include the following:
- All information about your company has to be verifiable.
- The business has to have received significant coverage from reliable sources.
That sounds a whole lot like E-E-A-T, right? This is why it is hard to fake authority. Having a Wikipedia page can help improve your perceived authority, but you can’t get a Wikipedia page unless you already are perceived as an authority!
You can find out a lot about Google’s assessment of authority of a site, including whether they have a Wikipedia page by looking at their About This Result information. There’s more here if you want to play around with this:
If all of the top ranking sites for your keywords are recognized as authorities by Wikipedia and granted their own page, and your site does not have one, there is a good chance that you’re going to struggle to rank for these keywords.
3) Get mentions on authoritative sites
This is probably the most important aspect of Google E-E-A-T. The “A” in E-E-A-T, meaning “Authoritativeness” is most likely influenced by your authoritative mentions.

I asked Gary about E-A-T. He said it's largely based on links and mentions on authoritative sites. i.e. if the Washington post mentions you, that's good.
He recommended reading the sections in the QRG on E-A-T as it outlines things well.@methode #Pubcon
— Marie Haynes (@Marie_Haynes) February 21, 2018
As mentioned previously, Google is getting much better at determining which mentions across the web truly are votes for your business. If a link or a mention is easy for you to obtain because you have provided content, paid for the link, or in some way incentivized the site owner to link to you, most likely, this mention is not the kind that would be used as a signal in Google’s systems that contributes to your E-E-A-T.
Links can be powerful if they truly are mentions from authorities in your niche or represent recommendations from experts. But Google is getting much better at determining which links are just there because an SEO is trying to trick their algorithms into thinking others are recommending content.
Legitimate mentions can contribute to your E-E-A-T. When Barry Schwartz mentions me on SERoundtable, that likely helps improve the information in the world to support my perceived authority on the topic of SEO.

Good authoritative mentions are usually difficult to get. But, if you want to be known as an authority, it is vitally important that you find ways to get them.
Good authoritative mentions often are like good Public Relations (P.R.) You want people to be mentioning your business in a positive light. The more good discussion you can generate about your business the better. This likely contributes to E-E-A-T.
Note from Marie: If you have struggled to find good link builders, you are not alone. It is easy to build links. It is very difficult to find ways to truly get other experts and authorities to mention you online. I do not offer link building, but if you need help here, you can reach out and I am happy to introduce you to someone whom I feel does good work in this area.
QRG example of an author with good E-E-A-T
In the QRG, they give this as an example of an author who has good E-E-A-T:
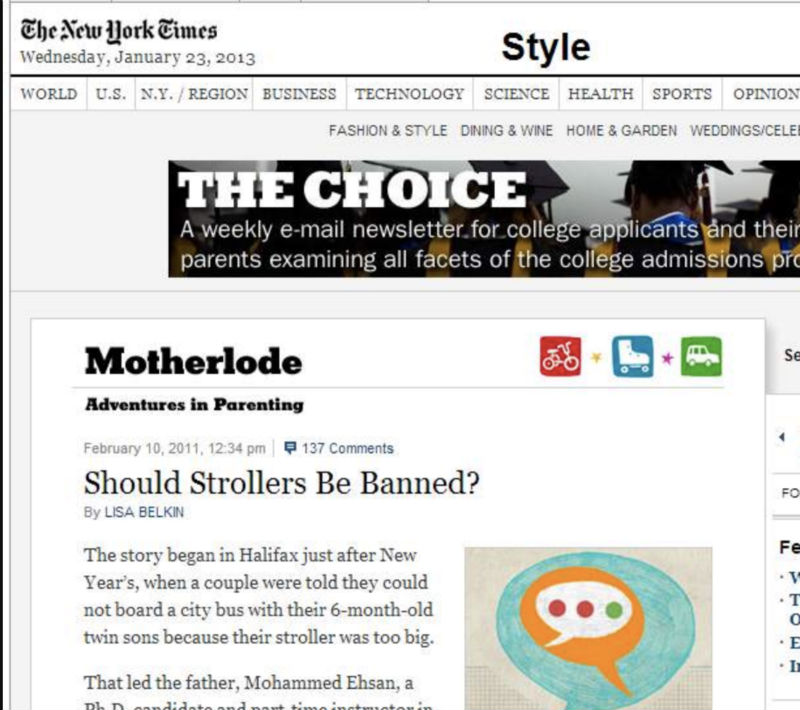
Remember when we Googled the name of the author who did not have E-E-A-T to write about the flu? When you Google the name of the author in this example, you can see that she is mentioned all over the place, on authoritative sites, in connection with parenting:
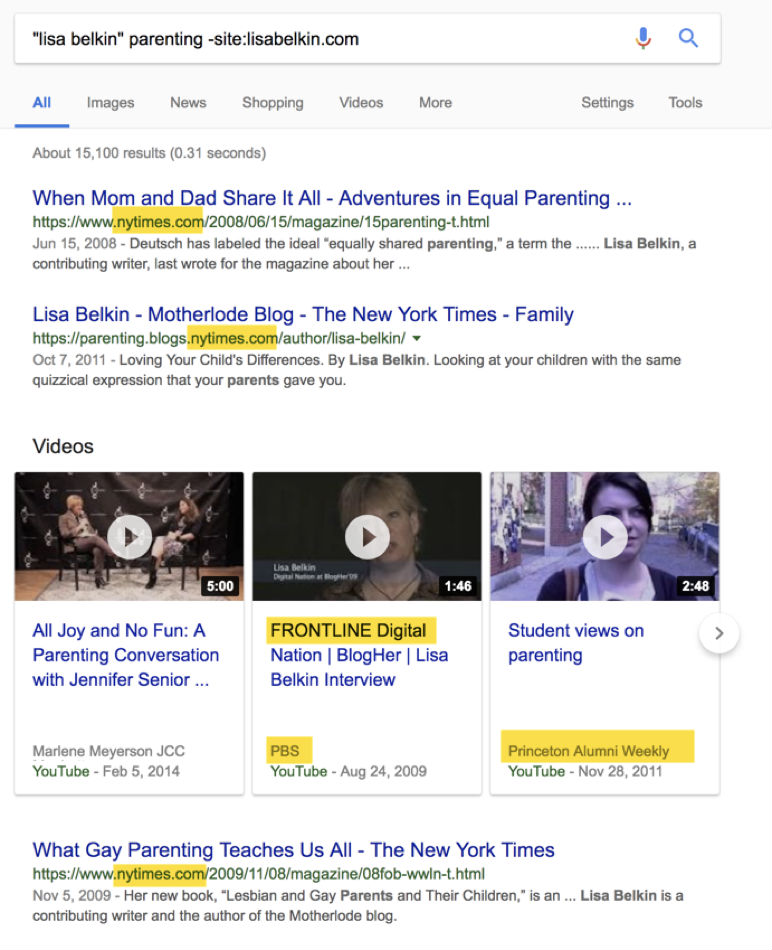
And here is what the QRG say about this author:

She is known as an expert on parenting issues.
It is not enough to just have experience, in order to have good E-A-T, you also need to be known online as an authority in your field.
If you are struggling to get authoritative mentions, here are some ideas that may help:
- Publish original research. This often will get mentions from authoritative places.
- Summarize current scientific research. Let’s say you have a site that sells products for diabetics. Let’s also say that new research has just emerged that explains in great scientific detail a new treatment for diabetes. You can take that information and use your personal expertise to explain it in layman’s terms. This often attracts links and mentions.
- Connect with journalists on HARO or via Twitter. Your goal is to get your name mentioned in connection with a topic discussed on an authoritative site. Be judicious. You can get links from journalists who happily link out which will likely accomplish little. Or, you can work to connect with journalists who really are publishing content that people find helpful.
- Create connections with people who are known as authorities in your field. You would not believe how many emails I get from people whom I have never heard of who want me to promote or link to their latest blog post. The people who have a much better chance of getting my attention are those whom I have met in person at a conference, or have had good discussion with online. You will have better success in getting links and mentions if you can truly develop good relationships with influencers in your field. To get mentioned by others, you need to get known by others.
4) Get mentions on forums
This may not be applicable to every business, but if people all over the web are raving about your competitors, then you want to have the same thing be true of your business as well. It may seem ludicrous for me to suggest that forum mentions can help improve your rankings. After all, this is something that could be easily gamed. However, this is what the QRG say:

I believe that it is not difficult for Google to determine which forum mentions are worthy of contributing to E-E-A-T and which ones are not. For several years, my main line of work was in doing link audits. I have seen thousands of forum mentions created just for links. It is usually quite easy for me to determine whether the chatter is real or whether it is artificially generated by an SEO. But being mentioned in legitimately helpful discussions may contribute to your E-E-A-T.
Why would Google look at forum information? Think of how you search and value first hand expertise. A few years ago I had the privilege of speaking at the RD Summit which was held in Florianopolis, a beautiful island in the south of Brazil. When I researched Florianopolis I started by looking at sites like Wikipedia. But, the most helpful information came from me reading the user generated content on sites like Reddit, Trip Advisor and other discussion forums.
If your competitors are being discussed in forums all over the place, and you are not, then most likely, you are not as well recognized as an authority.
While I do not recommend spamming forums, I do think that we should all be monitoring the internet for discussions about our brands. If there are negative discussions happening online, then jump in and try to rectify the problems. If people have questions that you could answer, then join the discussion and get your brand known. But be careful not to spam or annoy users.
5) Be trustworthy
One large change that Google made to their algorithms was noticed by SEOs in a core algorithm update the SEO community called “Medic”. Just prior to this update, Google released a new version of the Quality Raters’ Guidelines. While a lot of things changed in this version, the most notable, in our opinion, is the addition of the words “safety of users”. The highlighted words below were added to the QRG just prior to the Aug 1, 2018 update.
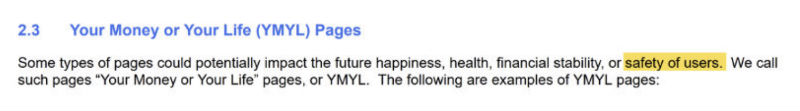

The wording has changed slightly in the most recent publication of the QRG as the words “of users” have been removed from the above paragraph. But, safety is still important. E-A-T is strongly connected to safety.
With the August 1, 2018 update, and again with other core updates that followed, we saw that sites that dropped in rankings consistently had issues with trust. These included things like the following:
- Loads of negative reviews online.
- Customers complaining about not being able to get a refund.
- Medical articles that had no scientific references, or that were making claims that contradicted current scientific consensus.
I have written a very thorough article on Trust and how it relates to E-A-T. I would encourage you to read this article if you want more information on how Google likely algorithmically determines trust and how you can improve on this metric.
6) Do all that you can to demonstrate your E-A-T on your website. Consider schema
While Google has told us that E-A-T is mostly determined via off-site links and mentions, we feel that we have seen improvements by extolling your E-A-T on your website. We like to see this type of information on both the homepage and your About page.
SameAs schema may help Google connect the dots in determining who your authors are and where they have been mentioned that is authoritative.
There is much more to know about schema, especially in regards to the topic layer of the knowledge graph. I recently created a guide with my updated thoughts on schema for 2024 for readers of my paid newsletter, Marie’s Thoughts.
Is E-A-T a ranking factor?
E-A-T should not be thought of as a ranking factor. But this does not negate its importance in Google’s algorithms!
A ranking factor is a single particular piece of data that Google can use in their algorithms that determine ranking.
As we saw above, Google says expertise, trust and authoritativeness is used for every single query for every result. Google’s HJ Kim described E-A-T as a template they use to rate sites. Google’s How Search Works documentation, tells us that for every search, after Google finds content in their index that is relevant, they next “identify signals that can help determine which content demonstrates expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness.” They say that doing this is what helps them determine which content is likely to be the most helpful.
E-A-T is not a ranking factor. As HJ Kim said, it is a core part of Google’s metrics. It is a template they use to rate every single site for every single query.
It is vitally important we pay attention to everything Google tells us about E-A-T.
Here is what Google says about whether E-A-T is a ranking factor
“Since we originally wrote this post, we have been occasionally asked if E-A-T is a ranking factor. Our automated systems use a mix of many different signals to rank great content. We’ve tried to make this mix align what human beings would agree is great content as they would assess it according to E-A-T criteria. Given this, assessing your own content in terms of E-A-T criteria may help align it conceptually with the different signals that our automated systems use to rank content.”
Sign up for Marie’s weekly newsletter – packed with tips to improve E-A-T and more
Some podcast episodes that may help
References
For a while, my team documented every single time Google discussed E-A-T. These may help:
July 2020
Google published documentation on how to rank in Discover, stating that “Our automated systems surface content in Discover from sites that have many individual pages that demonstrate expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness (E-A-T). Those looking to improve E-A-T can consider some of the same questions we encourage site owners to consider for Search. While Search and Discover are different, the overall principles for E-A-T as it applies to content within them are similar.”
June 2020
Great tips from Lily Ray on improving EAT for your authors.
May 2020
The May core update, released on May 4, 2020 appeared to once again reward websites with strong E-A-T. Something we noticed was that in many cases, sites that demonstrated real life expertise on a topic were rewarded. An example given in the article linked to, of a site that did well with this update would be an affiliate site that instead of just posting other people’s reviews, actually used the products themselves before publishing their review.
April 2020
Lily Ray wrote a great article, published on SEJ that will answer all of your questions about schema as it applies to your authors.
March 2020
Bill Slawski wrote an article for Search Engine Journal describing how Google can tell whether your content is expert written and the role this could play in determining E-A-T.
February 2020
This Bill Slawski article tells us that Google could be using something called Website Representation Vectors as a way to help measure E-A-T.
September 2019
Marie’s Whiteboard Friday with Moz discusses E-A-T and the Quality Raters Guidelines.
Google announces their partnership with the Mayo Clinic. This is interesting as this could impact health SERPs. It could be possible that Google is mandating only trustworthy health site, which aligns with our theory on how Google could measure scientific consensus and whether alternative health sites could be suppressed.
Marie sits down with Barry Schwartz to discuss algo updates, E-A-T, and penalties (video)
August 2019
Listen to Marie discuss the June Core Update with Authority Labs! (video)
Catch Marie talk about E-A-T, the Quality Raters Guidelines and more on her recent Digital Rage Podcast.
A leaked document shows more evidence of Google trying to algorithmically fight against sites contradicting scientific consensus (which in our opinion is what Google is trying to do with health sites in the June 3, 2019 Google update). If you’re a paid subscriber to our SEO newsletter, then you can get some of our detailed opinions on how this could be suppressing sites that contradict scientific consensus.
John Mueller talks about how Google tries to look at E-A-T for medical sites. John confirmed that they do look at information such as the author, the site overall, and reviewers partially through the content. He also recommends that you find an approach primarily for users, so it might not be best to hide it in structured data.
Google’s blog covers the topic: What webmasters should know about Google’s core updates. MHC was fortunate enough to earn a link from Google (to this very page) which provided additional reading for webmasters.
July 2019
From Google: Would a federal medical centre benefit from adding doctor author bios? John Mueller says if the work has been written or reviewed by an expert, it makes sense to indicate this. Here is his exact response: “I I think that’s something that you probably have answered already in that if you’re providing information on your webpage and it is kind of checked or written/created by someone who has a lot of knowledge on that topic then that’s something I would definitely highlight.”
Are you a health/medical site with content written without relative medical expertise? You can improve your content, remove or, or noindex it. Should you want to improve it, John says that having a medical expert on hand is a good idea.
Author E-A-T: It is possible to rank using a pseudonym? John Mueller once again hints that yes it is possible as Google’s algo’s likely do not judge the realness of author names used. He also noted the complexities with understanding a name which was a rather fascinating read.
How established are you in your niche and what are people saying about you? Google may be looking at prominence and what others are saying about you.
John Mueller discusses authorship and E-A-T in relation to using pseudonyms.
New info from a Google employee on the power of authority. This article from The Guardian says due to the rise in US school shootings, they’ve tweaked the algorithm to allow for adjustments to authority.
June 2019
John Mueller says in a Help Hangout that if you’ve seen a drop and you’re worried about E-A-T, you should work on increasing overall site quality.
Google rewards reputable reporting says the Economist. The study reveals that Google does indeed assess E-A-T on a site.
May 2019
Google confirms that they worked on improving medical search results in 2018. John also confirms that E-A-T is an important component to work on for medical sites.
Pedros Dias provides a great indication via Twitter regarding what composes quality. Check this out!
Building Trust for Your Service Area Business (article).
Possibly a minor quality update on May 9, 2019 . Many of our clients who have been working on E-A-T related changes saw slight increases on May 9. However a few saw slight decreases. We think that this was potentially a refresh of some sort in which Google re-assessed E-A-T signals for many sites.
Google’s new portal for How News Works (+touches on how E-A-T is a factor). Basically it says, “…our systems are designed to identify signals that can help determine which pages demonstrate expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness on a given topic, based on feedback from Search raters. Those signals can include whether other people value the source for similar queries or whether other prominent websites on the subject link to the story.”
Interesting note from John Mueller in a Hangout. John says that it’s not impossible for a distributor to outrank a manufacturer. It boils down to value, quality, technical standpoint, and authority!
Great E-A-T reminder courtesy of Lily Ray: if you Google your “company’s name + scam” and you see legitimate results on page 1, this can impact your organic performance. Consider engaging in a reputation management program (and obviously do some soul searching to see why customers consider you a scam)!
Bill Slawski discusses Trust Metrics at Google (article).
April 2019
Re: the March core update: John Mueller says to definitely check out the Panda questions from 2011 (more guidance on building high-quality sites). He also suggests that webmasters read the Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG) to understand what Google deems high versus low quality. This was such in important tip, John mentioned just days later that once again you should gather feedback from real users and read the Panda questions.
In a hangout, John says that for new sites, you won’t be an expert from day one. There’s no magic trick to appear to be an expert in Google’s eyes. Just work hard to have more expert-level content over time. Be an authority on a topic.
John Mueller regarding the March Core Update said, on the one hand, technical SEO issues are always smart to fix, but if the overall view of the site makes it hard to tell you’re an expert, then that can play a role as well
Advanced Search Summit tip: The website reputation matters. Google looks at words that co-appear with your brand name
March 2019
Danny Sullivan preannounced a significant core quality update (March 12, 2019) which later was coined by Google as the “March Core Quality Update”. I wrote an article for Search Engine Land that provided many examples of sites that saw noticeable improvements with this update and also included the types of changes that these sites made).
February 2019
A possible small quality update on February 27, 2019 provided nice improvements to clients of our were working on E-A-T related changes. This was likely a general quality update.
Stone Temple (now part of Perficient Digital) released an excellent article titled ‘Why Google’s Search Quality Raters Guidelines Matter to Content Marketers – Here’s Why #203’. The article clearly lays out why you should be paying attention to E-A-T.
Google releases a whitepaper which basically confirms that E-A-T is incredibly important.
A possible small quality update on February 16, 2019 resulted in many of our clients who were working on quality improvements see small positive changes. In our opinion, we feel that this was likely a re-assessment of E-A-T for many sites.
Gary Illyes in his Reddit AMA says that E-A-T is connected to links (although states that that is an oversimplification).
Gary Illyes in his Reddit AMA says that relevance is something they are constantly trying to figure out and that is evolving rapidly. However he references the QRGs twice stating that that is the process through which they evaluate if the algorithm is doing what they want it to do.
January 2019
January 31, 2019 was no a suspected update date, but some large sites saw major drops (for example, Irs.com (not .gov)) on this date. We think that this could reflect Google’s assessment of the “T” (Trust) in E-A-T.
John Mueller says it’s hard to measure author E-A-T algorithmically. A lot of things are soft quality factors that Google tries to figure out.
December 2018
Part 1 of 3 of Marie’s E-A-T webinar is available. It covers the basics of E-A-T. What is it? Is Google using it algorithmically? And it wraps up with audience questions. Check out our video and transcript to see it in full.
An algorithm update from December 4-6, 2018 (likely a mild quality update) resulted in further drops for many sites with previous E-A-T related issues. There was no obvious pattern as to what was addressed with this update but we felt there was a link component to it based on the fact that many clients who we recently filed disavows for saw gains.
November 2018
An algorithm update from November 23-26, 2018 — which we suspect was a core quality update — resulted in many gains for our clients who had been working hard to improve their E-A-T.
Debate begins on whether Google uses information from the BBB as a ranking factor. Marie joins the discussion on the 15th.
October 2018
An algorithm update on October 31, 2018 appeared to be a significant core quality update. Many sites that saw drops on August 1, 2018 or September 27, 2018 saw further drops on this day. We saw a couple of clients who have worked hard to improve “trust” (the “T” in E-A-T) make nice improvements.
John Mueller reinforces that we should be doing more to promote author E-A-T including adding author schema.
Having a physical address isn’t always a sign of trust. It is often used this way for pure eCommerce sites and if your top competitors all have a valid address listed on their site.
Cyrus Shepard shares great tip for keeping an eye on your E-A-T.
September 2018
Google confirmed that an algorithm update but called it “small”. On the dates of September 24-27, 2018 (and continuing into October) we saw some really significant changes in sites we monitor. It looked to be a tweak on the August 1 “Medic” update. Danny Sullivan of Google later confirmed that this was a broad core quality update and that it would roll out into October.
Google confirms in a blog post that authority is a ranking factor, saying, “For starters, the authority of a web page is now a more important signal in the ranking.”
John Mueller said in a hangout that an author bio can be helpful to include on your site. Specifically he said, ““Often times, it makes it a little bit easier for users to understand the context of whatever you’ve written. If you have a link to an author profile that shows you really know what you’re talking about, you go to conferences, you’ve written about this is different places on the web. This gives them more trust in your content on the web. All of these things might be reasons why you might have an author profile page you link from your content.”
August 2018
John Mueller made some comments in a hangout about Google’s Quality Raters’ Guidelines and how they relate to author E-A-T. He talks about how E-A-T is a factor rather than seeing this explicitly to rank your website.
There was a massive August 1 update likely related to E-A-T. Many sites in the health/wellness/medical space were heavily impacted, and was thus nicknamed the Medic Update, however this was not the only industry to be affected. There are also reports of non-YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) sites being affected as well. In my opinion, this is the biggest update we have had in a long time.
July 2018
Great E-A-T idea from Marie RE: vet open house day.
June 2018
A great E-A-T developing idea from Marie inspired by Lululemon.
Marie suggests, following a case study, that social mentions can increase your E-A-T.
Link building tip for E-A-T inspired by Domino’s filling potholes.
May 2018
There was a quality update. At MHC, we saw some clients who had been working on improving E-A-T see nice gains.
Can social mentions improve E-A-T? In this newsletter episode, we give an example of a brand that found a way to make a crazy product go viral. We do believe that large amounts of positive social mentions can help improve Google’s assessment of your brand’s authority.
April 2018
An algorithm update on April 16, 2018 may have been a tweak to the way in which Google algorithmically assesses E-A-T. We saw improvements for clients’ sites that had been working on E-A-T improvement.
A new Google patent, written about by Bill Slawski talks about a new way in which Google can calculate PageRank so that link equity only passes through trusted pages. Most likely, those trusted pages are pages that have good E-A-T.
March 2018
An algorithm update on March 7-9 was confirmed by Google. Google confirmed that this update was primarily about relevancy. Many sites that were affected had E-A-T issues.
Customer testimonials can help improve Google’s assessment of Trust for your site. Here is a great article by Joel Klettke on how to get high quality testimonials.
Gary Illyes from Google said at Pubcon Austin that Google’s algorithmic assessment of E-A-T is largely based on links and mentions on authoritative sites.
December 2017
A significant algorithm update on December 26, 2017 affected sites with E-A-T issues.
An update on December 12, 2017 occurred which appeared to be a significant algorithm update, dubbed the “Maccabees update”. We have noticed that many sites that were hit were sites that were hit with quality updates, and believe that a big component of this update dealt with E-A-T.
November 2017
Google started showing new information in knowledge panels to show a publisher’s awards, and reviewed claims. This shows us that Google can determine information about awards (which speaks to trust) algorithmically.
October 2017
An algorithm update on October 28-29, 2017 seemed to affect sites with E-A-T issues.
An algorithm update on October 8, 2017 happened. We saw nice improvements in a couple of clients’ sites who had worked to improve the E-A-T of individual authors.
September 2017
An algorithm update on September 6-8, 2017 happened. We saw good improvements for a site that had been working at improving E-A-T.
July 2017
In my newsletter I shared about how you can determine what industry Google thinks you are in. It is then important to make sure you have E-A-T for that industry. For example, if Google has you classified as a medical site, but you have no authors with medical experience, this could make ranking in your space difficult.
March 2017
Fred update (March 7-8) – This was a major quality update. It appears to have affected sites that existed primarily for SEO reasons. I also think that at this time Google tweaked the algorithm to reward sites with good E-A-T (Experience, Authority and Trust).
February 2017
Large core algorithm update. This update affected a lot of sites. I saw several sites that I think dropped in rankings because of a lack of E-A-T (Experience, Authority and Trust).
About Marie
 Dr. Marie Haynes is recognized as a leader in the SEO industry and has 10+ years of experience helping businesses of all sizes improve their site quality. She is a frequent contributor to Moz.com and Search Engine Watch and a regular speaker at Pubcon and SMX. Marie was named one of the top five industry influencers by Rand Fishkin, founder of Moz, and constantly stays up to date with changes to Google’s algorithms to the benefit of her clients. To contact Marie, visit the contact page. For media Inquiries, click here.
Dr. Marie Haynes is recognized as a leader in the SEO industry and has 10+ years of experience helping businesses of all sizes improve their site quality. She is a frequent contributor to Moz.com and Search Engine Watch and a regular speaker at Pubcon and SMX. Marie was named one of the top five industry influencers by Rand Fishkin, founder of Moz, and constantly stays up to date with changes to Google’s algorithms to the benefit of her clients. To contact Marie, visit the contact page. For media Inquiries, click here.





